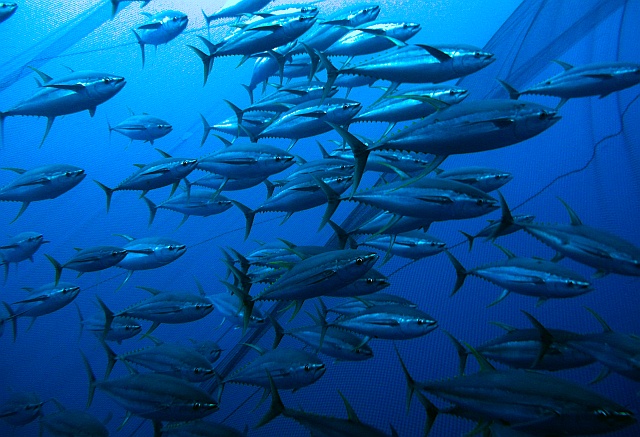
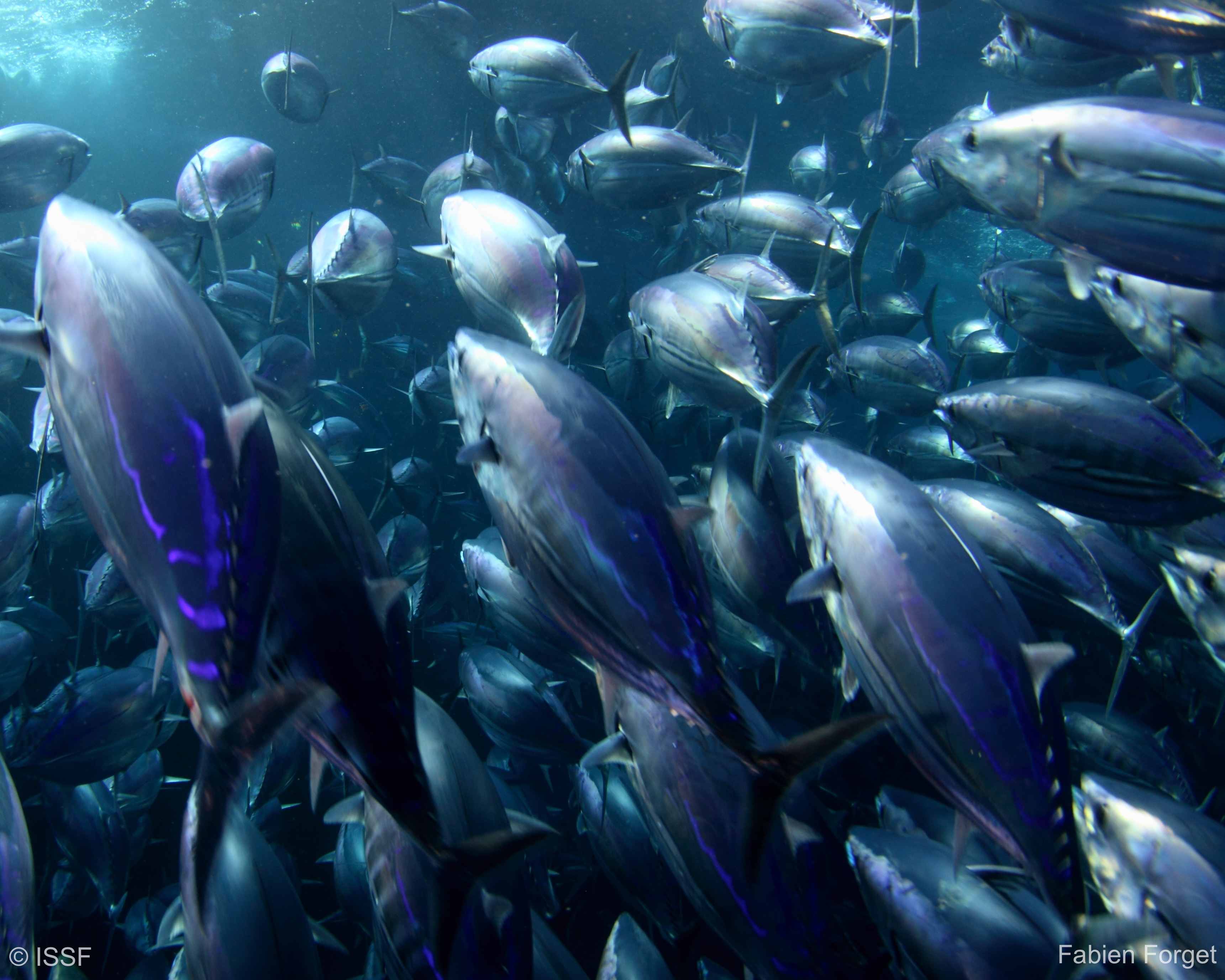
Southern Bluefin
Southern bluefin tuna (Thunnus maccoyii) was the first of the three bluefin tunas to be recognized as a distinct species.
In: FAO Species Catalogue, Vol. 2. Scombrids of the World (1983). Courtesy of Fisheries and Aquaculture Department/Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
Like the other bluefin tunas (T. thynnus and T. orientalis), Southern bluefin reaches large sizes: adults commonly grow to 180 cm in length.
Thunnus maccoyii is found in the Southern Hemisphere in the temperate and cold waters of the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific oceans. Southern bluefin’s thermoregulation capacity enables it to tolerate water temperatures from more than 25°C in the subtropics to less than 3°C in the sub-Antarctic regions. Southern bluefins migrate vast distances and tend to form schools by size, especially when they are juveniles and during the spawning season.
Species Characteristics
| Size (cm) | Weight (kg) | Age (yrs) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Common | 160 | 180 | 14+ |
| Maximum | 245 | 260 | 40 |
| Maturity | 120–150 | 100–160 | 8–12 |
| Generation Length |
12 |
Geographic Limits
- Thunnus maccoyii is found in the Southern Hemisphere of the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans.
- Its geographical range varies between 30°S and 50°S, to nearly 60°S.
Species Management
- Thunnus maccoyii is assessed and managed by the Commission for the Conservation of Southern Bluefin Tuna (CCSBT) RFMO.
- The other tuna RFMOs — Inter-American Tropical Tuna Commission (IATTC), International Commission for the Conservation of Atlantic Tunas (ICCAT), Indian Ocean Tuna Commission (IOTC), and Western and Central Pacific Fisheries Commission (WCPFC) — defer to CCSBT for the management of Southern bluefin.
Bluefin Tuna Stock Status
Our Status of the Stocks report summarizes the status of bluefin tuna worldwide according to the most recent scientific assessments.
It also reviews the management measures for bluefin that Regional Fisheries Management Organizations (RFMOs) have adopted.
RELATED RESOURCES

Interactive Stock Status and Catch Tool
Use our interactive data-visualization tool to create and then download or share graphics on tuna stock status.
You can visualize data on 23 commercial tuna stocks (by species and ocean area) share of total catch, stock health trends, and catch trends over time.

ISSF 2025-08: An Evaluation of the Sustainability of Global Tuna Stocks Relative to Marine Stewardship Council Criteria
The Marine Stewardship Council scoring system was used to evaluate 23 stocks of tropical and temperate tunas, including the bluefin tuna stocks (added in 2021), throughout the world.
Bluefin Stock Health & Catch Trends
Use our “Interactive Stock Status and Catch Tool” to visualize, download, and share data about bluefin tuna:
- Stock health since 2011
- Current catch by fishing method
- Catch trends by fishing method since 1950
Tuna Conservation
Our research and advocacy work aims to ensure, on a global level, that tuna resources are well managed and protected from overfishing.
Tuna Stock Evaluations
An ISSF report uses the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) scoring system to evaluate both the health and RFMO management of 23 tuna stocks worldwide, including bluefin.


